WNoDeS Workflow
Standard Worker Node (WN) and Virtual Worker Node (VWN) can coexist together. The Bait (wnodes_bait) is a process acting as a batch job attractor. Jobs requiring to be executed over non-virtual machine (if the mixed mode is enabled) are handled as a standard job of batch system. The worker node resources are dynamically modified in order to reflect the real availability of the host, which needs to keep in consideration the resources allocated for the execution of the Virtual Machines (VM). The other jobs dispatched on the Bait are immediately suspended. The Hypervisor (HV) instantiates the VM by using the requested virtual image and the job execution is migrated on the VM.
WNoDeS process flow for batch
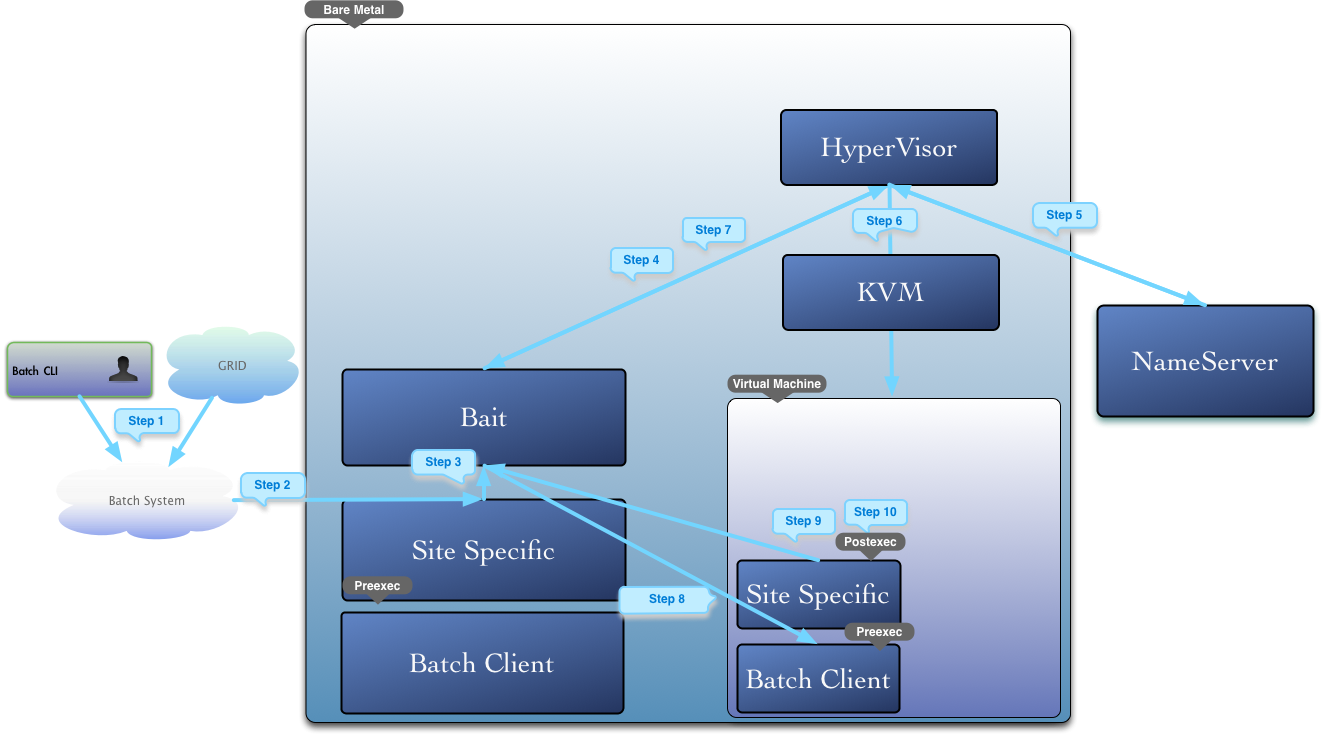 Figure 1 - The WNoDeS process flow.
Figure 1 - The WNoDeS process flow.
Figure 2 describes the process flow for a batch job that needs to be dispatched from the Batch System to a virtual computing resource - known as virtual job. A job is received by the Batch System, through whatever method is supposed (e.g., local or Grid job submission). At this point the following steps are followed:
- the Batch System dispatches the job to be executed on a WN under the WNoDeS control containing HV and Bait services;
- the WN receives the job. A pre-execution script stops the job, gets the job's requirements (e.g., required RAM);
- the pre-execution script sends a notification message to a process called Bait running on the WN, advising on a new job to process;
- the process Bait running on the WN evaluates if the job needs to run on and asks the HV if the job's requirements are available;
- the HV contacts the central Nameserver (NS) service to obtain a lease hostname for the VM
- the HV creates a VM for job execution using the KVM stack;
- the HV notifies Bait when the VM is ready;
- the Bait migrates the job to the VM provided by the HV;
- the job goes through a second pre-execution script on the VM, which notifies the Bait that the job has started;
- when the job finishes, a post-execution script on the VM notifies the Bait;
- the Bait delivers the VM and waits for a new job.
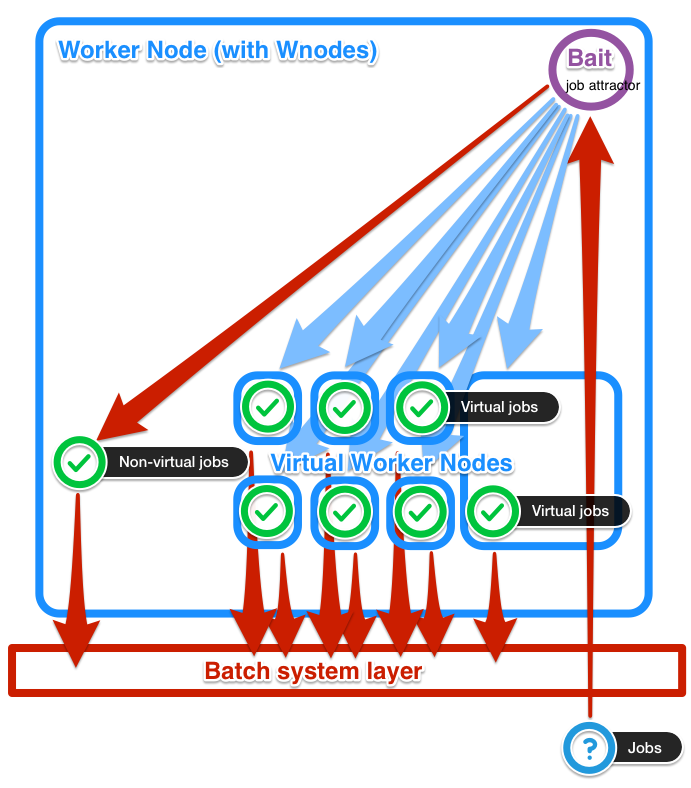
Figure 2 - Job dispatching.