System administration guide
Index
- WNoDeS components.
- Installation Prerequisites.
- Installation Recommendations.
- Nameserver Configuration.
- Manager Configuration.
- Hypervisor Configuration.
- Bait Configuration.
- Site Specific Configuration.
- WNoDeS Processes.
- LSF Batch System Configuration.
WNoDeS components
WNoDeS is characterized by the following components:
bait, hypervisor, manager, nameserver and site-specific.
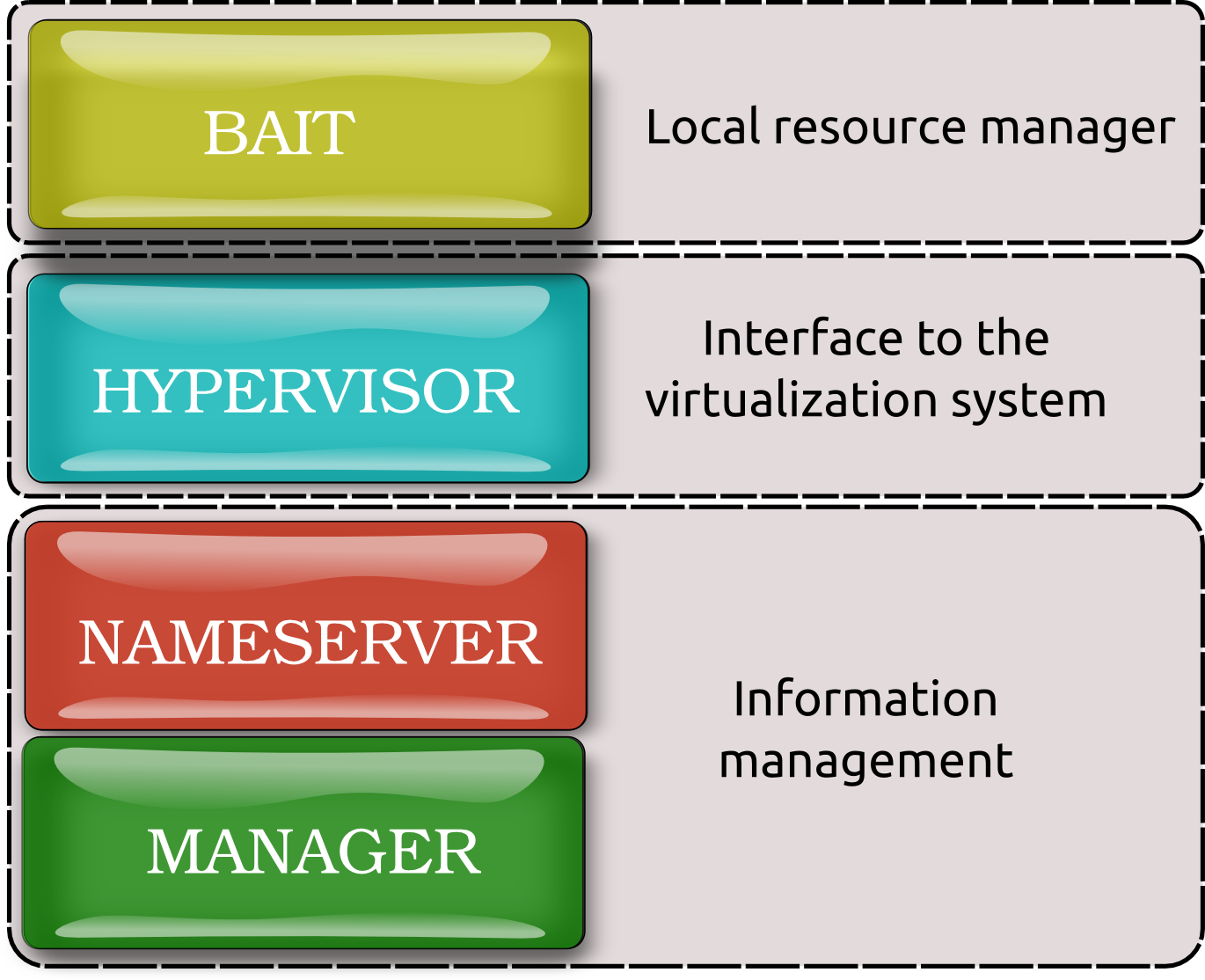
Figure 1 - The overall WNoDeS components
Bait is the host resource manager responsible for verifying that there are resources to execute both real jobs and virtual jobs, requiring the instantiation of the virtual machine when necessary, and executing the job on the suitable resource;
Hypervisor is mainly the interface to the virtualization system responsible for instantiating virtual machines where the virtual job will be executed. However, if the mixed mode feature is enabled, it is also able to run real job;
Nameserver, Manager can be considered as the information management.
The nameserver is a sort of catalogue responsible for keeping trace of all the virtual machines currently running for each hypervisor, and all the virtual machine images stored in the configured repository
(see Installation Prerequisites).
The manager is a Command Line Interface (CLI) that is responsible for the configuration of the repository of the virtual machine images.
It provides a set of options to handle images, VLANs, hostnames, bait and hypervisor configuration files.
Furthermore, it supports a set of options that manage bait and hypervisor status.
Overview of WNoDeS Deployments
WNoDeS can be differently deployed on a given site in relation to its needs.
However, both physical and virtual machines need to be prepared.
Figure 2 shows the WNoDeS deployment with the mixed mode enabled.
In this case the wnodes_bait service is installed and configured on the same host of the wnodes_hypervisor service.
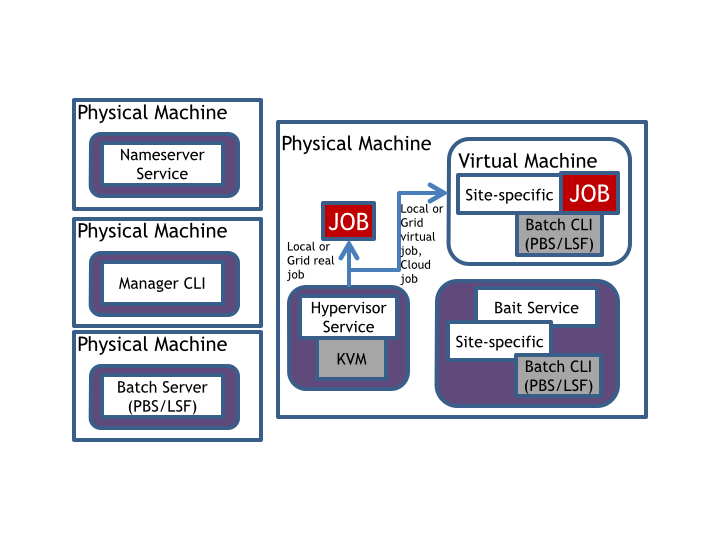 Figure 2 - Example of deployment
Figure 2 - Example of deployment
Installation Prerequisites
Operating System
All WNoDeS components are certified to work on Scientific Linux SL5 x86_64 and SL6 x86_64 with EPEL as repository for external dependencies.
DNS
Full access to the DNS configuration is needed in order to add each virtual machine hostname, which is used to instantiate a virtual resource.
Host resolution will be used by DHCP to provide ip address to the virtual resource.
The hostname for the wnodes_bait service should contain 'bait' in case of Mixed Mode disabled.
DHCP
Full access to the DHCP configuration is needed in order to configure the mapping from MAC address to hostname for each hostname that is used to instantiate virtual machine.
KVM
KVM needs to be installed on all the nodes where the hypervisor service runs.
Repository Distribution
A dedicated repository for the virtual machine images needs to be configured. It could be a Web Server or a shared file system such as the common NFS, Lustre and GPFS. In the former, a http repository needs to be configured.
Image
Use virtio driver to define the image.
Batch System
The batch system either LSF or Torque/Maui needs to be installed and configured.
In case of PBS, the Computing Elements, worker nodes and submission nodes are configured to allow ssh connection without requiring password: each worker node could login without password to the Computing Element and among worker nodes.
It is suggested to put the same ssh host keys in all the nodes (i.e., both bait and worker node) in order to easy the managing of the host list.
Installation Recommendations
Nameserver
The wnodes_nameserver service can be installed on any machine that is not used as hypervisor. It can be both virtual or physical. This service contains the configurations of hypervisor and bait.
Please use the following package:
wnodes_nameserver
Log files are produced under /var/log/wnodes/nameserver. Standard error and standard output files are produced under /tmp.
Manager
The wnodes_manager CLI can be installed on any machine or laptop.
Please use the following package:
wnodes_manager
Hypervisor
The wnodes_hypervisor service can be installed on any machine, where the virtualization technology is enabled. As detailed in (see Quick Start Guide), the behaviour of the wnodes_hypervisor service depend on the mixed mode feature:
If the feature is not enabled, then the wnodes_hypervisor service will instantiate a virtual machine that contains the wnodes_bait service. Therefore, the image of that virtual machine needs to be created with the bait software and added to the WNoDeS repository before starting the wnodes_hypervisor service.
If the feature is enabled, the wnodes_hypervisor service will be able to execute jobs.
Please use the following package:
wnodes_hypervisor
Log files are produced under /var/log/wnodes/hypervisor. Standard error and standard output files are produced under /tmp.
Bait
As detailed in (see Quick Start Guide), the installation and configuration of the wnodes_bait service depend on the mixed mode feature:
- If the feature is not enabled, then the wnodes_bait service will run on a virtual machine that is automatically instantiated by the wnodes_hypervisor service.
- If the feature is enabled, the wnodes_bait service will run on the same machine where the wnodes_hypervisor service runs.
Please use the following package:
wnodes_bait
Log files are produced under /var/log/wnodes/bait. Standard error and standard output files are produced under /tmp.
Site specific
The wnodes_site_specific component contains, among other things, the wnodes_preexec script that sends a request to the wnodes_bait service in order to instantiate a virtual machine that can be used to execute a job.
The wnodes_preexec script and its configuration file need to be present on the machines where jobs are executed. In case of a shared FS, the wnodes_preexec script and its configuration file can be copied in a common area: otherwise, you need to install them in all the machines specifying the same configuration file.
Please use the following package:
wnodes_site_specific
Debug Log file is produced under /tmp with the name
Nameserver Configuration
The wnodes_nameserver configuration files that need to be edited are:
- MAC list file
- wnodes hypervisor file
- wnodes bait file
WNoDeS nameserver MAC list file
The /etc/wnodes/nameserver/mac_list.ini file has an INI format in which each section corresponds to a given VLAN and the content of each section shows details of the specified VLAN. The file contains the following information:
[<VLAN_NAME>]
network_type = OPEN
bait_host = <fully bait hostname>^00:16:3e:01:00:16;...
vm_host = <fully virtual image hostname>^00:16:3e:01:00:16;...
where
network_type can have the OPEN value or the CLOSE value (see Description of Network Type Values);
bait_host is a list of values separated by ; whose value expresses hostname and mac address linked by the ^ symbol.
If the mixed mode feature is enabled, bait_host can be empty;
vm_host is a list of values separated by ; whose value expresses hostname and mac address linked by the ^ symbol.
All the hostnames must be defined in the DNS, while the mac addresses with the related IP addresses in the DHCP.
Description of Network Type Values
OPEN It means that the related VLAN is able to access to the local network.
CLOSE It means that the related VLAN is able to access to the external network and disable to access to the local sub networks.
It is defined for the network isolation of the virtual machine in order to open to the network of virtual machine externally but not internally.
Typically virtual machine that is used to run jobs has the network_type value set to OPEN.
WNoDeS hypervisor file
The /etc/wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_hv_config.ini file has an INI format. The file contains the following information:
[HV_CONF]
HV_PORT=8222
BAIT_PORT=8111
LOG_FILE_NAME=wnodes_hv.log
MAX_LOG_FILE_SIZE=100000
MAX_COUNT_LOG_FILE=5
LOCAL_REPO_DIR=/etc/wnodes/repo
BAIT_IMG_TAG=<image tag>
BAIT_VM_RAM=800
HOST_GROUP_<ALL>=
ENABLED_VLAN_GROUP_<ALL>=DEFAULT_VLAN
SSH_KEY_FILE=/etc/wnodes/hypervisor/.ssh/hv_id_rsa
USE_LVM=YES
VOLUME_GROUP=vg0
SERVICE_NIC_IP=<IP NIC Service>
SERVICE_NIC_IP_MASK=<MASK IP NIC Service>
DNS_RANGE=<DNS RANGE 1,DNS RANGE 2>
DNS_LEASE_TIME=5m
where HV_CONF is the name of the section that contains the following options:
HV_PORT specifies the port of the wnodes_hypervisor service;
BAIT_PORT specifies the port of the wnodes_bait service;
LOG_FILE_NAME specifies the logging file name;
MAX_LOG_FILE_SIZE specifies the maximum size of the logging file name.
The size is expressed in Byte;
MAX_COUNT_LOG_FILE specifies the maximum number of rotations of the logging file name.
The value 5 means that after 5 rotations the first is removed;
LOCAL_REPO_DIR specifies the repository directory of images that the wnodes_hypervisor service download;
BAIT_IMG_TAG specifies the tag name of the virtual machine associated to the bait.
The wnodes_hypervisor service will get the image of the virtual machine related to the tag.
The value of this option is only considered with mixed mode disabled;
BAIT_VM_RAM specified the amount of RAM to allocate in the virtual machine where the wnodes_bait service will run.
The value of this option is only considered with mixed mode disabled.
The following two options need to be specified in pair:
HOST_GROUP_<ALL>specifies a set of regular expressions separated by ;. It represents groups of hostnames that belong to given VLANs withas its logical name; ENABLED_VLAN_GROUP_<ALL>specifies the enabled VLANs for the logical name that are associated to groups of hostnames. Please use DEFAULT_VLAN to refer to the VLAN of the wnodes_hypervisor service;
SSH_KEY_FILE is the location of the rsa key that is created by the wnodes_hypervisor service during its start and saved there;
USE_LVM is a flag whose value can be yes or no.
If it is yes, this means that the wnodes_hypervisor service will define and create a file system to be associated to the virtual machine that will be instantiated.
LVM stands for logical volume;
VOLUME_GROUP specifies the name of the volume group to be set before creating the logical volume;
SERVICE_NIC_IP specifies the physical address of the wnodes_hypervisor interface used to interact with the virtual machine;
SERVICE_NIC_IP\_MASK specifies the mask address of the wnodes_hypervisor interface used to interact with the virtual machine;
DNS_RANGE specifies the range of the addresses that the DHCP server can assign to the virtual machine.
This option starts with DNS because the service used to change the DHCP is called dnsmasq;
DNS_LEASE_TIME specifies the time in which the address is not used.
After that the address is used for another virtual machine.
WNoDeS bait file
The /etc/wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_bait_config.ini file has an INI format. The file contains the following information:
[BAIT_CONF]
BATCH_SYSTEM_TYPE=<Type of the batch system>
HV_PORT=8222
BAIT_PORT=8111
LOG_FILE_NAME=wnodes_bait.log
LOGGING_LEVEL=INFO
MAX_LOG_FILE_SIZE=100000
MAX_COUNT_LOG_FILE=5
HOST_GROUP_<ALL>=
ENABLED_VLAN_GROUP_<ALL>=DEFAULT_VLAN
VM_UNREACH_TIMEOUT=200
STATUS_RETRY_COUNT=3
SCHEDULING_INTERVAL=60
RESERVATION_LENGTH=1200
USE_LVM=YES
TYPE=<Types of request>
PX_FAILED_RETURN_STATUS=1
DEFAULT_VM_IMG=
DEFAULT_VM_MEM=2000
DEFAULT_VM_CPU=1
DEFAULT_VM_BANDWIDTH=50
DEFAULT_VM_STORAGE=10
DEFAULT_JOB_TYPE=<Type of request>
MAX_VM_MEM=3000
MAX_VM_BANDWIDTH=100
MAX_VM_CPU=8
MAX_VM_STORAGE=100
MIN_VM_MEM=1500
MIN_VM_BANDWIDTH=10
MIN_VM_CPU=1
MIN_VM_STORAGE=10
MIXED_MODE=yes
where BAIT_CONF is the name of the section that contains the following options:
BATCH_SYSTEM_TYPE specifies the type of batch system.
If it is set to LSF, the batch system will be LSF.
If it is set to PBS, the batch system will be Torque/Maui;
HV_PORT specifies the port number of the wnodes_hypervisor service;
BAIT_PORT specifies the port number of the wnodes_bait service;
LOG_FILE_NAME specifies the logging filename;
LOGGING_LEVEL Can be one of DEBUG, CRITICAL, ERROR, WARNING, INFO, and specifies the amount of logging information to print.
MAX_LOG_FILE_SIZE specifies the maximum size of the logging filename;
MAX_COUNT_LOG_FILE specifies the maximum number of rotations of the logging file name.
The value 5 means that after 5 rotations the first is removed;
The following two options need to be specified in pair:
HOST_GROUP_<ALL>specifies a set of regular expressions separated by ;. It represents groups of hostnames that belong to given VLANs withas its logical name; ENABLED_VLAN_GROUP_<ALL>specifies the enabled VLANs for the logical name that are associated to groups of hostnames. Please use DEFAULT_VLAN to refer to the VLAN of the wnodes_hypervisor service;
VM_UNREACH_TIMEOUT represents the default timeout in seconds that is used when the instantiated virtual machine is unreachable (e.g., the instantiate virtual machine can be unreachable because the DHCP service has not provided the correct address.).
After having reached the specified timeout, the virtual machine is destroyed and then created again;
STATUS_RETRY_COUNT is the number of times a virtual machine can stay on the same status.
After that the request is rejected; %The instantiation of a virtual machine is crossed by several states.
SCHEDULING_INTERVAL is the interval of the batch system to schedule new jobs;
RESERVATION_LENGTH is used when the batch system is LSF.
It represents the length of the reservation;
USE_LVM specifies if the wnodes_hypervisor service creates the LVM for each virtual machine.
If it is set to NO, then the wnodes_bait service will not consider the storage resource.
The mandatory resources are: CPU, RAM, network and storage;
TYPE is a list of types of requests that the wnodes_bait service can accept to create virtual machines.
The possible types are BATCH,
and BATCH_REAL separated by ;.
If it contains BATCH, then the bait service will accept batch jobs.
If it contains BATCH_REAL, then the bait service will accept real jobs;
PX_FAILED_RETURN_STATUS represents the return status of the preexec service in order to send the job, which the virtual machine has been created for, in the queue of the batch system.
In case of LSF the value is greater than 0, while for PBS the value is greater than 2;
The following default values represent the default values of the virtual machine parameters when they are not specified in the request:
DEFAULT_VM_IMGis the default value of the virtual machine image;DEFAULT_VM_MEMis the default value of the virtual machine memory;DEFAULT_VM_CPUis the default value of the virtual machine cpu;DEFAULT_VM_BANDWIDTHis the default value of the virtual machine bandwidth;DEFAULT_VM_STORAGEis the default value of the virtual machine storage;DEFAULT_JOB_TYPEis the default value of the virtual machine image;
The following maximum values represent the values that can be specified in a request:
MAX_VM_MEMis the maximum value of the virtual machine memory;MAX_VM_BANDWIDTHis the maximum value of the virtual machine bandwidth;MAX_VM_CPUis the maximum value of the virtual machine cpu;MAX_VM_STORAGEis the maximum value of the virtual machine storage;
The following minimum values represent the values below which the bait service cannot accept requests to instantiate virtual machines, that is the set batch system does not consider this particular bait able to accept new jobs:
MIN_VM_MEMis the minimum value of the virtual machine memory;MIN_VM_BANDWIDTHis the minimum value of the virtual machine bandwidth;MIN_VM_CPUis the minimum value of the virtual machine cpu;MIN_VM_STORAGEis the minimum value of the virtual machine storage;
MIXED_MODE specifies if the mixed mode feature is enabled.
WNoDeS nameserver state
/var/log/wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_ns_state
Manager Configuration
The wnodes_manager configuration file that needs to be edited is /etc/wnodes/manager/wnodes.ini. It has an INI format and contains the following information:
[NAMESERVER]
NS_HOST=<myhost>.<mydomain>
NS_PORT=8219
where NAMESERVER is the name of the section that contains the following options:
NS_HOST is the fully qualified hostname where the wnodes_nameserver service runs;
NS_PORT is the port number where the wnodes_nameserver service runs.
Options to handle virtual machine images
The Manager CLI is responsible for the configuration of the repository of the virtual machine images. The repository is composed of files.
This CLI associates a tag to each virtual machine image file: however, more tags can be linked to the same virtual machine image file. The WNoDeS core services use this tag when they need to refer to a given virtual machine image file. The tag represents the unique identifier of the virtual machine image.
A tag is defined by the following parameters:
tag is a string that specifies the tag.
Please use the following convention to specify the tag:
<name>_<os>_<arch>
where name is the name of the virtual machine image file, os is the operating system included in the virtual image file, arch is the architecture of the operating system.
location can take the values:
http, file
Please use file for local filesystem or filesystem mounted locally (e.g., gpfs), while use http for web repository.
path is a string that specifies the address of the virtual machine image file.
arch can take several values such as:
i386, i686, x86\_64.
It specifies the architecture of the virtual machine image file.
type can take several values such as:
raw, qcow2, bochs, cloop, cow, dmg, iso, qcow, vmdk, vpc.
It specifies the format of the virtual machine image file.
dev is the root file system of the image that will be used by the libguestfs package.
Please provide at least one image to the WNoDeS system. In this case the WNoDeS system will take care of tag's changes (and caching) automatically.
This CLI handles the following options in relation to the image:
-a/--add_image {tag location path arch type: the option, followed by an ordered-parameters list separated by a space, adds information about the virtual machine image file.
--purge_image_list removes all the images information from the repository.
Please be careful.
-d/--delete_image {tag}: the option, followed by the tag parameter, deletes the tag and all the other information associated to the tag.
-g/--get_image_info {tag}: the option, followed by the tag parameter, gets information about the virtual machine image file identified by the specified tag.
-l/--list_image lists information about the registered virtual machine image files.
-r/--replace_image {tag location path arch type}: the option, followed by an ordered-parameters list separated by a space, replaces information about the virtual machine image file.
Options to obtain VLANs information
This CLI provides system administrators with options to retrieve information about VLANs that are specified in the /etc/wnodes/nameserver/mac_list.ini file. Below these options are detailed:
-V/--list_vlan provides a list of the VLANs registered in the current configuration.
-B/--list_baitname {vlan}: the options, followed by the vlan name, provides a list of the bait hostnames registered in a specific VLAN configuration.
For example:
BAITNAME=vwn-0001-bait.infn.it MAC= 00:16:3e:00:00:01
-L/--list_hostname {vlan}: the options, followed by the vlan name, provides a list of the virtual machine hostnames registered in a specific VLAN configuration.
For example:
HOSTNAME= vwn-0001.infn.it MAC= 00:16:3e:00:00:01
-N/--list_network_type {vlan}: the options, followed by the vlan name, provides information about the network type (e.g., open/closed) of a specific VLAN.
-O/--list_option_values {option vlan}: the option, followed by an ordered-parameters list separated by a space, provides information about the values of the given option for the specified VLAN.
This option is useful to handle new options in the /etc/wnodes/nameserver/mac_list.ini file that do not have a specific method in the code.
--remove_unused_hypervisor {hostname}: the option, followed by the hostname, takes away the hypervisor from the list of the manage, and remove every virtual machine hostnames assigned to the specific hypervisor.
Options to modify the registered hostnames
The following options change the /etc/wnodes/nameserver/mac_list.ini file in order to modify the registered hostnames:
-A/--add_hostname {hostname vlan}: the option, followed by a virtual machine hostname with the mac address and a vlan name, adds the virtual machine hostname to the specific vlan.
-T/--add_baitname {baitname vlan}: the option, followed by a bait hostname with the mac address and a vlan name, adds the bait hostname to the specific vlan.
-D/--delete_hostname {hostname vlan}: the option, followed by a virtual machine hostname with the mac address and a vlan name, deletes the vitual machine hostname from the specific vlan.
-E/--delete_baitname {baitname vlan}: the option, followed by a bait hostname with the mac address and a vlan name, deletes the bait hostname from the specific vlan.
In order to actuate the following options, the wnodes_nameserver must be stopped after any change and its status file (/var/log/wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_ns_state) must be deleted. Warning: as consequence the status of the deployed bait hostnames and virtual machine hostnames will be lost. For this reason, it is highly recommended to stop all the hypervisor services before restarting the wnodes_nameserver service.
Options to manage the configuration files of the wnodes_bait and wnodes_hypervisor services WNoDeS
provides centralized configuration files (that are identified with the /etc/wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_hv_config.ini file and /etc/wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_bait_config.ini file) for all the wnodes_hypervisor and wnodes_bait services. These files can be verified and modified by using the following options:
-v/--list_hv_config lists the values of the options specified in the wnodes_hypervisor configuration file.
-b/--list_bait_config lists the values of the options specified in the bait configuration file.
-P/--replace_hv_config {option value}: the option, followed by the option name and its value, replaces the value of the option in the wnodes_hypervisor configuration file.
-p/--replace_bait_config {option value}: the option, followed by the option name and its value, replaces the value of the option in the wnodes_bait configuration file.
The changes will affect all the new deployed wnodes_hypervisor and wnodes_bait services* **and the old if rebooted TO BE CHECKED.
Tip: in order to reload any change in a specific service configuration, the reload_host_config option can be used.
Options to manage the wnodes_bait and wnodes_hypervisor status
The status of the wnodes_bait and wnodes_hypervisor services are handled by using the following options:
-o/--get_config {host port}: the option, followed by the hostname and port values, contacts the relative server and asks the current configuration.
-s/--get_bait_status {host}: the option, followed by the bait hostname value, gets the status for the specified bait.
The value can also contain a regular expression.
-S/--get_hv_status {host}: the option, followed by the virtual machine hostname value, gets the status for the specified wnodes_hypervisor;
-R/--reload_host_config {host port}: the option, followed by the virtual machine hostname and port values, reloads the configuration of the specified service;
-t/--hv_connection {host}: the option, followed by the wnodes_hypervisor hostname value, gets the virtual machine connected to the specified wnodes_hypervisor service.
The value can contain 'all': in this case the option will return all the deployed wnodes_hypervisor hostnames and their virtual machine hostnames;
--bait_connection {host}: the option, followed by the bait hostname value, gets the virtual machine connected to the specified bait service.
The value can also contain a regular expression;
-w/--open_bait {host}: the option, followed by the bait hostname value, changes the status of the bait service in OPEN_ADMIN;
-x/--close_bait {host (or 'all' or regular expression)}: the option, followed by the bait hostname value, changes the status of the bait in CLOSED_ADMIN.
The value can contain 'all' or a regular expression;
-X/--destroy_VM_instance {vm_hostname}: the option, followed by the virtual machine hostname value, destroys and removes the specified virtual machine instance;
--list_available_hostname gets the available virtual machine hostnames (not yet assigned);
--list_available_baitname gets the available bait hostnames (not yet assigned);
--list_active_hostname get the active virtual machine hostnames;
--list_active_baitname get the active bait hostnames;
--ping {hostname port}: the option, followed by the hostname and port values of one of the WNoDeS services among wnodes_hypervisor, wnodes_nameserver and wnodes_bait, returns the version of the correspondent WNoDeS service.
Hypervisor Configuration
The wnodes_hypervisor configuration files that need to be edited are:
- /etc/wnodes/hypervisor/wnodes.ini
- /wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_hv_config.ini that is on the machine where the wnodes_nameserver service runs. The information contained in the file is loaded by the wnodes_hypervisor service when it contacts the wnodes_nameserver service.
wnodes hypervisor conf
The /etc/wnodes/hypervisor/wnodes.ini file has an INI format and contains the following information:
[NAMESERVER]
NS_HOST=<fully nameserver hostname>
NS_PORT=8219
where NAMESERVER is the name of the section that contains the following options:
NS_HOST is the fully qualified hostname where the wnodes_nameserver service runs;
NS_PORT is the port number where the wnodes_nameserver service runs.
Bait Configuration
The wnodes_hypervisor configuration files that need to be edited are:
- /etc/wnodes/bait/wnodes.ini
- /etc/wnodes/nameserver/wnodes_bait_config.ini that is on the machine where the wnodes_nameserver service runs. The information contained in the file is loaded by the wnodes_hypervisor service when it contacts the wnodes_nameserver service.
During its execution the /log/wnodes/hypervisor/hv_network_current_status file is created. It is on the same machine where the wnodes_hypervisor service runs. WARNING: this file is internal to the wnodes_hypervisor and cannot be removed.
wnodes bait conf
The /etc/wnodes/bait/wnodes.ini file has an INI format and contains the following information:
[NAMESERVER]
NS_HOST=<fully nameserver hostname>
NS_PORT=8219
where NAMESERVER is the name of the section that contains the following options:
NS_HOST is the fully qualified hostname where the wnodes_nameserver service runs;
NS_PORT is the port number where the wnodes_nameserver service runs.
Site specific Configuration
Each wnodes_preexec script has the /etc/wnodes/site_specific/wnodes_preexec.conf file as configuration file, whose name and location can be renamed and changed according to the site. In case of LSF this file needs to be copied in the \$(LSF_ENVDIR)/scripts directory.
The /etc/wnodes/site_specific/wnodes_preexec.conf file has an INI format and contains the following information:
[general]
TMPFILE=/tmp/my_bait
LOCAL_DOMAIN =<domain name>
NS_HOST=<fully nameserver hostname>
NS_PORT=8219
[batch]
FAIL_RETURN_STATUS = 3
TYPE = PBS
[default]
TYPE=<type of request>
IMG=<tag name>
NETWORK_TYPE=<type of network>
CPU=1
MEM=2500
STORAGE=30
ENABLEVIRTIO=YES
BANDWIDTH=10
PX_SCRIPT=
[<user_name>|<unix_group_name>]
TYPE=<type of request>
IMG=<tag name>
NETWORK_TYPE=<type of network>
CPU=1
MEM=2700
STORAGE=30
ENABLEVIRTIO=YES
BANDWIDTH=10
PX_SCRIPT=
VM_CONFIG_MOUNT_113-MOUNT=ce02-lcg.cr.cnaf.infn.it:/etc/grid-security /etc/grid-security
VM_CONFIG_USELVM_MOUNT=/dev/vdb /mnt
VM_CONFIG_USELVM_LINK=/mnt /tmp
\end{verbatim}
where there are at least three sections:
general is the section that contains basic options for the wnodes_preexec configuration:
TMPFILEspecifies the temporary file created by the wnodes_preexec script to provide the bait hostname that is managing the job;LOCAL_DOMAINspecifies the local domain;NS_HOSTspecifies the fully qualified wnodes_nameserver hostname;NS_PORTspecifies the port number of the wnodes_nameserver service;
batch is the section that contains the options for the batch_system configuration:
TYPEis the type of batch_system used. Its value can be:PBS, LSF
FAIL_RETURN_STATUSrepresents the failed status returned by the wnodes_preexec script. In case of LSF the value is 1, otherwise it is greater than 1.
default is the section that contains default options for a given request received by the px:
TYPEis the type of request that the wnodes_preexec can support. The possible types are BATCH, and BATCH_REAL. If it contains BATCH, then the request will contain batch jobs. If it contains BATCH_REAL, then the request will contain real jobs;IMGis the unique identifier of the virtual image. It specifies the image that the px can request in order to be instantiated by the wnodes_hypervisor;NETWORK_TYPEcan be the OPEN value or the CLOSE value (see Description of Network Type Values);CPUis the value of the virtual machine cpu;MEMis the value of the virtual machine memory;STORAGEis the value of the virtual machine storage;ENABLEVIRTIOspecifies if any driver for the interface virtualization is enabled. Its value can be:YESorNOBANDWIDTHis the value of the virtual machine bandwidth;PX_SCRIPTis the wnodes_preexec script that is executed on the virtual machine to guarantee some settings like the FS presence.
<user_name>|<unix_group_name> is the section that contains options that identify a type of VM associated to that name.
So all the requests coming from the user will have instantiated the same type of VM.
However, a user can submit a different request specifying parameters in the batch job script submission.
TYPEis the type of request that the wnodes_preexec can support. The possible types are BATCH, and BATCH_REAL. If it contains BATCH, then the request will contain batch jobs. If it contains BATCH_REAL, then the request will contain real jobs;IMGis the unique identifier of the virtual image. It specifies the image that the px can request in order to be instantiated by the wnodes_hypervisor;NETWORK_TYPEIts value can be:OPENorCLOSE(see Description of Network Type Values);CPUis the value of the virtual machine cpu;MEMis the value of the virtual machine memory;STORAGEis the value of the virtual machine storage;ENABLEVIRTIOspecifies if any driver for the interface virtualization is enabled. Its value can be:YESorNOBANDWIDTHis the value of the virtual machine bandwidth;VM_CONFIG_MOUNT_113-MOUNTspecify that the specified directories will be mounted on the virtual machine;VM_CONFIG_USELVM_MOUNTspecify that the /dev/vdb will be mounted on the /mnt;VM_CONFIG_USELVM_LINKspecify that the /dev/vdb will be linked on the /mnt.
In case of PBS set the prologue in all bait nodes as follows:
$> cat /var/torque/mom_priv/prologue
#!/bin/bash
while [ ! -f /usr/bin/wnodes/site_specific/wnodes_preexec ]; do sleep 3 ; done
sleep 10
/usr/bin/wnodes/site_specific/wnodes_preexec -f /etc/wnodes/site_specific/wnodes_preexec
--jobid $1 --username $2 &> /root/prologue.txt
$> chmod 500 /var/torque/mom_priv/prologue
$> chmod 500 /usr/bin/wnodes/site_specific/wnodes_preexec
In case of PBS configure the epilogue in all WN nodes:
$> chmod 500 /var/torque/mom_priv/epilogue
$> chmod 500 /usr/bin/wnodes/site_specific/wnodes_postexec
WNoDeS Processes
wnodes_nameserver
The wnodes_nameserver service delivers the hostnames specified in the given batch system. It starts getting two input arguments:
-d that is used to start wnodes_nameserver as a service.
the /etc/wnodes/nameserver/mac_list.ini file that contains the list of hostnames that the wnodes_hypervisor service associates to the virtual machines. For each hostname the relative mac address is specified.
and using the following command:
service wnodes_nameserver start
During its execution the /var/local/wnodes/wnodes_ns_state.ini file is created.
Once having copied your virtual image files in the repository that you have already defined and configured, the wnodes_nameserver service will be populated with all the information on the relevant virtual images by doing as follows (as detailed in Section~\ref{sec:manager}):
wnodes_manager -a <tag> <location> <path> <arch> <type>
wnodes_hypervisor
The wnodes_hypervisor service starts using the following command:
service wnodes_hypervisor start
At the start the wnodes_hypervisor service performs the following steps to get the state of the network configuration:
it discovers the default ethernet that can be eth0 or eth1* of the **wnodes_hypervisor hostname;
it extracts the IP address of the default ethernet;
it creates a default bridge identified with br.default to support default VLAN;
it associates to the default bridge the IP address of the default ethernet;
it modifies the default gateway in order to be the created default bridge.
Doing so the wnodes_hypervisor service is able to instantiate virtual machines that belong to the same VLAN of the wnodes_hypervisor hostname and also to other VLANs. Therefore, to allow the wnodes_hypervisor service to instantiate virtual machines that belong to VLANs that are different compared to the VLAN of the wnodes_hypervisor hostname, the other VLANs need to be configured on the switch and the network configuration of the wnodes_hypervisor hostname needs to be changed in order to configure a bridge for each new VLAN. Then, if the \texttt{wnodes_hypervisor} service receives the request to instantiate a virtual machine that belongs to a different VLAN, the wnodes_hypervisor service will create a dedicated bridge for the VLAN identified with \texttt{br.VLAN}, the relative virtual ethernet interface for the VLAN identified with eth.VLAN and the link to the bridge.
The wnodes_hypervisor hostname has a private network interface. The service bridge allows the wnodes_hypervisor hostname to have a point to point connection with all the virtual machines it supports. Doing so the virtual machine is able to contact the wnodes_hypervisor service by using the private interface of the wnodes_hypervisor hostname without accessing the switch.
wnodes_bait
The wnodes_bait service starts using the following command:
service wnodes_bait start
wnodes_manager
Remember to destroy VM as following:
wnodes_manager -X <VM name>
LSF batch system configuration
The LSF configuration files that need to be edited are:
- cluster file
- batch site host file
- batch site queue file
Verify the setting of the LSF_ENVDIR environment variable.
LSF cluter file
Add in the LSF cluster configuration file all the hostnames that WNoDeS will use to instantiate machines by editing the file $(LSF_ENVDIR)/lsf.cluster.<cluster-name>
as follows:
HOSTNAME model type server r1m mem swp RESOURCES
<virtual machine hostname> ! ! 1 3.5 () () ()
where:
HOSTNAMEspecifies the name of the hostname;modelspecifies CPU type;typespecifies the type of architecture. If it is set to !, than the architecture is determined by the batch system;serverrun job;r1mdetermines the load every minute;RESOURCESspecified the resources specified on the machine.
Also, in the Host section of the same file, all the hostname of both virtual machines and hypervisors should specify the vmid resource. For example, the following line:
vwn196-00 ! ! 1 3.5 () () (mg)
should be changed to:
vwn196-00 ! ! 1 3.5 () () (mg vmid)
LSF shared file
In the $(LSF_ENVDIR)/lsf.shared file, the following lines should be added to the “Begin Resource” section:
vmpref Numeric 15 Y (vms get preference)
vmid String 15 () (vmid)
Reconfigure lsf as follows:
lsadmin reconfig
Restart badmin as follows:
badmin mbdrestart
LSF batch site hosts file
Add in the LSF batch configuration file the same hostnames of above and define groups by editing the following file $(LSF_ENVDIR)/lsbatch/<custer-name>/configdir/lsb.hosts as follows:
HOST_NAME MXJ r1m pg ls tmp DISPATCH_WINDOW EXIT_RATE
<virtual machine hostname> 1 () () () () ()
...
GROUP_NAME GROUP_MEMBER
<group name> (<virtual machine hostname 1> <virtual machine hostname 2> ...)
where:
HOST_NAMErepresents the name of the hostname;MXJrepresents the max number of jobs that can be run on the hostname. If it is equal to !, the batch system will calculate the number;r1mpgrepresents the page rate;lstmpDISPATCH_WINDOWtells that the hostname can be used in the dispatched windowlEXIT_RATErepresents the max number of failures within a dispatched window before the closure of the job;GROUP_NAMEGROUP_MEMBER
Reconfigure lsf as follows:
lsadmin reconfig
Restart badmin as follows:
badmin mbdrestart
LSF batch site queues file
Define or modify a queue to associate hostnames to the cluster by editing the file $(LSF_ENVDIR)/lsbatch/<cluster-name>/configdir/lsb.queues as follows:
Begin Queue
QUEUE_NAME = wnodes_2_a
PRIORITY = 10
JOB_ACCEPT_INTERVAL = 0
PRE_EXEC = /usr/share/lsf/conf/scripts/wnodes_preexec
-f /usr/share/lsf/conf/wnodes_preexec
USERS = all
HOSTS = <virtual machine host 1> <virtual machine host 2> <machine host 1> ...
RES_REQ = select[type==any]
DESCRIPTION = Worker Node on Demand
End Queue
where:
QUEUE_NAMErepresents the name of the queue.PRIORITYis the batch system priority to decide which job can be run.JOB_ACCEPT_INTERVALdefines the time interval in second between the execution of two jobs on the same host: if it is equal to 0, than jobs are executed at the same time; if it is equal to 100, than the time that elapses between the execution of two jobs is 100.PRE_EXECrepresents the location of the pre exec path file.USERSrepresents the users that are enabled to use the queue.HOSTSspecifies the list of machines that are part of the queue.RES_REQselects machines: if it contains type==any, than it means that machines of any types (archi- tectures) will be selected.
Esb.conf
The file /etc/wnodes/site-specific/esub.conf should be edited to specify the queues handled by WNoDeS. For example, the following content:
[wnodes_08]
CONFIG_FILE=/usr/share/lsf/conf/wnodes_preexec_08.conf
says the the wnodes08 queue is under the control of WNoDeS, and its preexec use /usr/share/lsf/conf/wnodespre configuration file.
Additional files
The elim.vm, esub and esubscript.py files should be copied in $LSF_SERVERDIR.