Significant Features
VLAN support
WNoDeS provides the support to the use of VLANs, therefore Virtual machines running on the same hypervisor can belong to heterogeneous VLANs. Main advantages are:
- Minimize the network broadcast domain.
- Grant different network access polices to every virtual machine.
- Network isolation, this is an important feature for cloud computing, where users get root access to virtual machine.
Mixed Mode
The Mixed Mode [1] represents one of the main functionalities of WNoDeS. It was introduced to provide the ability to use every physical computing resource, both as hypervisor node to instantiate virtual machines and both as a traditional member nodes of the batch system. This way a physical node can host at the same time both traditional jobs, directly running in the real machine, and also virtual ones, running in a virtual node instantiated there by the hypervisor. The adoption of this functionality is optional and allows a computing centre to optimize the usage of its resources by integrating real and virtual resources. Both scenarios provide virtual machines that can be used to execute batch jobs, to perform analysis or to run applications. Through this feature it is possible to execute jobs with special requirements on the physical node, avoiding the limitation introduced by the virtualization. The typical jobs that request the enabling of the mixed mode are ones requiring GPU processing or high performance for the I/O components. Moreover, on the same physical node, provided it has enough memory, CPUs and disk, the mixed mode can also offer virtualized services for those users requiring them. The mixed mode mechanism handles users' requests in collaboration with the batch system. These can be traditional batch jobs requests, submitted locally or via grid: in this case by using the site-specific configuration file, the batch job can be executed either on the physical node or on the virtual machine.
These can be also cloud provisioning requests, submitted via the Cloud CLI or the IGI portal: in this case the provisioning will only be furnished by a virtual machine. WNoDeS translates these users' requests into jobs that are handled by the batch system.
This Mixed mode has been available since WNoDeS 2.0.0-2 in the EMI-2 Matterhorn distribution [2] whilst the Cloud CLI that interacts with the WNoDeS cloud platform has been released since the version WNoDeS 3.0.0-1 the EMI-3 Monte Bianco distribution [2].
Figure 1 shows how the mixed mode turned on works: the job in queue to the batch system is sent to the bait service that verifies the state of the virtual machines contacting the hypervisor service. In relation to the type of job and the site-specific configuration, the batch job will be executed on either virtual machine or physical one. The cloud job will be always executed on the virtual machine.
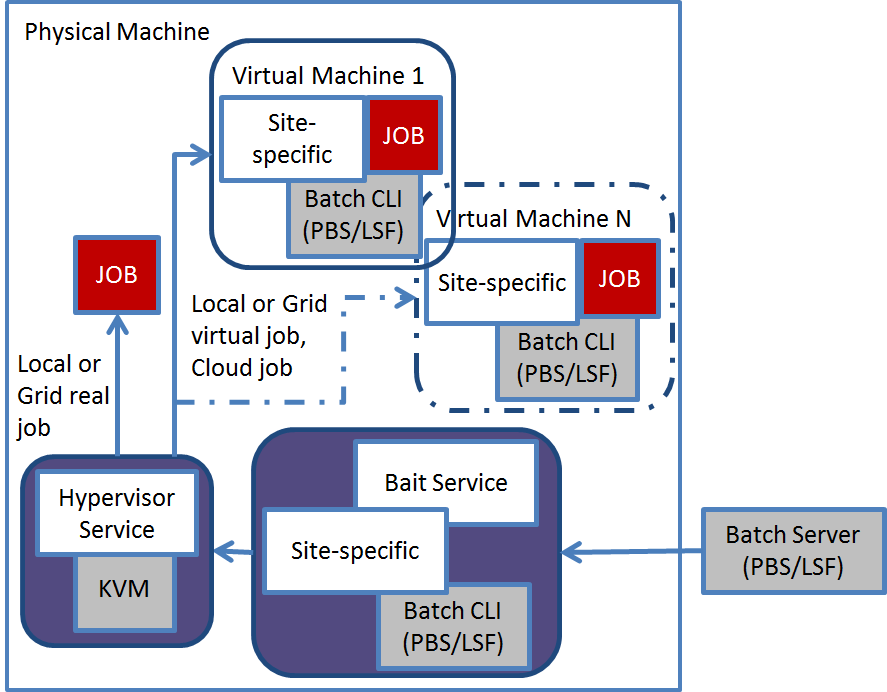 Figure 1 - Mixed mode turned on
Figure 1 - Mixed mode turned on
References
[1] Salomoni D., Italiano A. and Ronchieri E. WNoDeS, a Tool for Integrated Grid and Cloud Access and Computing Farm Virtualization, Journal of Physics: Conference Series Volume 331 Part 5: Computing Fabrics and Networking Technologies. 331, 2011
[2] Aiftimiei, C., Ceccanti, A., Dongiovanni, D., Di Meglio A., and Giacomini F. Improving the quality of EMI Releases by leveraging the EMI Testing Infrastructure. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 396:5, 2012.